What is an atom's electron configuration?
RECAP: Orbitals
Probability to find electron at a given orbital
Pauli's Exclusion Principle
2 electrons cannot have the same quantum numbers
Orbital Energy
Energy required to remove each electron from it's appropriate orbital (also known as ionization energy).
Aufbau relationship to periodic table
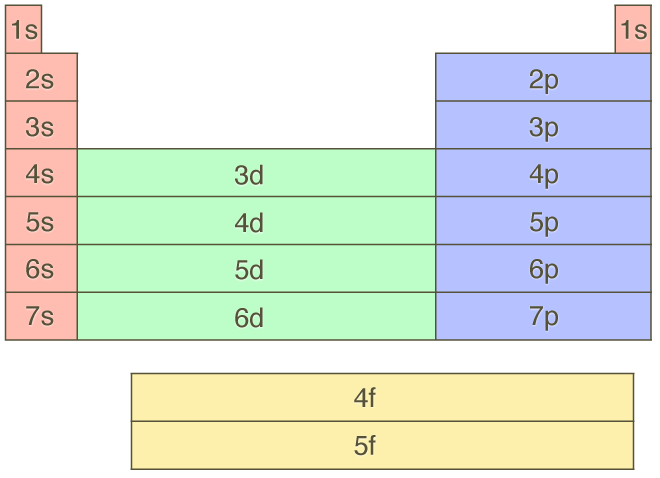
Aufbau Principle - order in which E are filled

Orbital Diagram
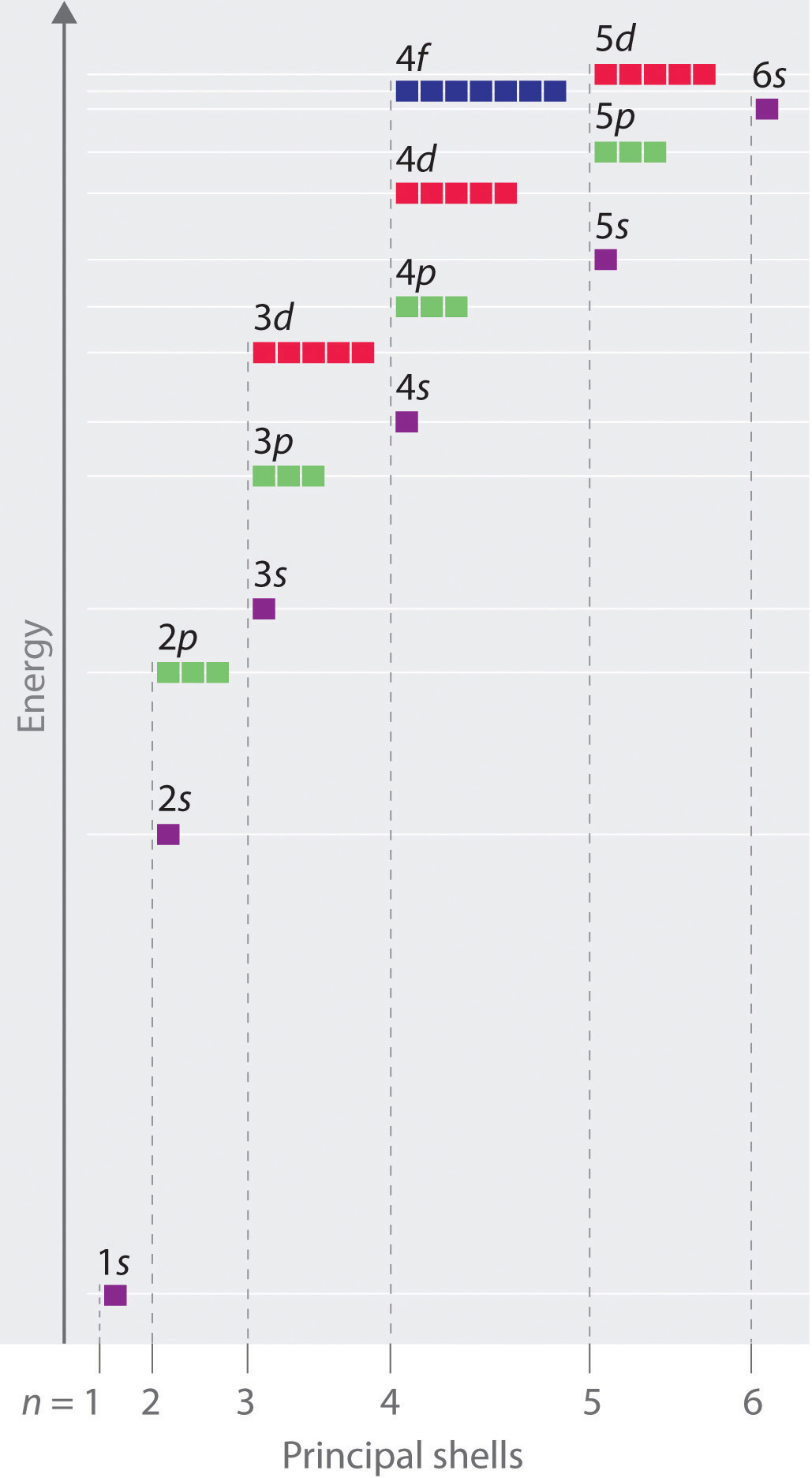
How are electrons orbitals filled?
Ex. C is 1s22s22p2
Stable Electron Configurations
Stable
- Filled shell is very favorable.
- (much weaker) Half-filled orbital - so one electron in each
Bonding
Unstable
Interaction between the outer (valence) electrons in order to lower their energy (completion of the shell)
Valence electrons
Outermost electrons:
Cl: 1s22s22p63s23p5
Ionic
Covalent
Metallic
Electron Property
Electron exchange
Nondirectional
Ex. NaCl, attracted to each other because Na becomes cation, Cl anion. Nondirectional because does not matter the angle which Na and Cl are at, only how close they are
Nondirectional
Ex. NaCl, attracted to each other because Na becomes cation, Cl anion. Nondirectional because does not matter the angle which Na and Cl are at, only how close they are
Electron Property
Electron sharing
Directional
Ex. ethane C2H6
Directional because each atom prefer to be at a specific direction
Directional
Ex. ethane C2H6
Directional because each atom prefer to be at a specific direction
Electron Property
Electron sharing
Nondirectional
Sea of electrons. Average electron density = # valence electrons!
Nondirectional
Sea of electrons. Average electron density = # valence electrons!
Ceramics
High melting points, brittle, etc
------------------------
| - + - + - + - + - + |
| + - + - + - + - + - |
------------------------
------------------------
| - + - + - + - + - + |
| + - + - + - + - + - |
------------------------
Electronegativity
Quantificaton of the element's desire for an electron (see pg 26 in book)
Electron screening: filled inner electron shells sort of block out the proton pull for the outer shelled electrons
Electron screening: filled inner electron shells sort of block out the proton pull for the outer shelled electrons
Properties
Conductivity, heat conduction bc of the sea of electrons. Malleability make sense too bc interaction is
Shiny bc sea of electrons
Shiny bc sea of electrons