General Pathology
Types of Necrosis
Coagulative
-Coagulation of proteins
- Most common
- Solid organs
-AI
- Paleness- no blood
-Infarct- No Nuclei
May see- Granulation tissue, Haemorrhage
Colliquative Necrosis
- Onlly in brain
- Autolysis to completion w/ little coag
- abscesses
see:
-bubbly appearancr
-accumulation of liquids
- loss of nuceli
- glial cells
- congested bv
- AI
Lungs/ respiratory
TB
Milliary
- Granulomatas the same size
- around bv
- thickened pleura
- CI
- caseous necrosis
- haemorrhage
-congestion
- giant cells
- fibroblasts, langerhans cells, macro, lymphs
Bronchopneumonia
-varying size tubrcules
- around airways
- thickened pleura
- CI
- caseous necrosis
- haemorrhage
-congestion
- giant cells
- fibroblasts, langerhans cells, macro, lymphs
Lobar
- all at the same stages
- Lung in tact
-puss
-haemosiderosis
- fibrin
-anthracosis
-consolidation
-AI
-Pleural thickening
pneumonia
Bronchi
- Different stages
- descrtruction of lung paranchymal
-patchy lesions
-puss
-haemosiderosis
- fibrin
-anthracosis
-consolidation
-scar tissue
-AI
-Pleural thickening
Anedomyosis
-type of choristoma
- see endometrial glands in myometirum surrounded by lamina popria
- CI
-haemorhage
Uterus
Breast
Fibroadenoma
-benign neoplasm
- thickening
- fibrocolagenous tumour
- more ducts than normal
- encapuslated tumour
-dialated ducts
- cystic dysplasia of glands
- congestion of BV
-CI
Fibroleiomyoma
- congestion
-capsules
-scar lesions
-fibranoid- in this see SMS, fibroblasts, collagen
- well differentiated growth
- -benign neoplasm
- congestion og BV
- casule formation
MORBID
-benign
-capsule
-smc,fibroblasts
-well differentated
- no evidence of invasion no necrosis
- no haemorrhage
Primary Adenocarcinoma
- coagulative necrosis
- Haemorrhage
- haemosiderin deposition
- congested BC
- fatty/hydrophic changes
- AI
- vascular sportus
-fibroblasts, collagen, macrophages
- makes gland like structures- adeno=gland
Healing Myocardial INFARCT
- Coagulative necrosis
- Haemorrhage
- haemosiderin deposits
- Congested BV
- fatty/ hydrophic changes
- AI
- vascular sprouts
- fibroblasts, collages, macrophages
- SEE MORE GRANUATION TISSUE
Heart
Skin/CT
12/7 wound healing
- very contracted wound
-sml scab
-sml exudate/ AI
- complete re epithelisation
- scar tissue
- giant cells
-granulation tissue
- vascular sprouts
- young collagen
3/7 wound healing
- AI under scab
-re epithelisation
- congested BV
- scab- fibrin, RBC, WBC, Dry exudate
- granulation tissue down low- new collagen, Mac's, plasma cels, new vascular sprouts.
Thyroid
Thyroid Hyperplasia
- enlargement
-heamorrhage
- flattened cuboidal cells
- enlarged colloid
- hyperplasia
-CI
Rheumatic Pancarditis
-AI- where organisation occurs
- Congested BV
- Aschoffs Nodules
- Aschoffs Giant cells
- degenerated collagen
- Fibrosis- CI seen here
Recent Myocardial Infarct
- coagulative necroisis
- haemorrhage
- haemosiderin deposit
- congested BC
- fatty/hydrophic change
- granulation
- AI
- SEE SCARING
Blood vessels
Recanalisng venous thrombus
- see thrombus in lumen- plts, fibrin, RBC
- Damaged intima
-Lines of Zahn (mixed thrombus)
- granulation tissue in periphery
- vascular sprouts
- dystrophic calcification
-scaring
Liver
Fatty change of the liver
- fatty change
- AI
- fibrosis- capsule
-coagulative necrosis
-choselstis
- thickened capusle
-hydrophic change
- nucleus pushed to side of cell
Brain/ neural
acute suppurative menangitis
- Congested BV
- colliquative necrosis
-fibrin
-thickened leptomeningies
-pressure atrophy
-AI
-oedema
-congested BV
Healing Cerebral Infarct- Gliosis
- congested BV
-AI
- oedema- fluid
- Colliquative necrosis
-gliosis ( proli. of glial cells)
- cystic space
-CI
- vascular sprout formation
Kidney
Kidney in hypertension (benign)
- arteriosclerosis
- fibrinoid necrosis
-elastosis
- protein cast formation
- CI
- Hyalinisation of Glomeruli
- atheromatus change (early)
-Haemorrhage
- Congestion of BV
Kidney in hypertension (entering malignant Phase)
- arteriosclerosis
- fibrinoid necrosis
-elastosis
- protein cast formation
- CI
- Hyalinisation of Glomeruli
- atheromatus change (early)
-Haemorrhage
- Congestion of BV
-ONION SKINNING
Atherosclerosis of Aorta
- Arheroscelrosis
- fibrous plaque formation
- medial atrophy and thinning
-intimal thickening
-fibroblast and leiomyocyte proliforation
- lipid infiltration
- congestion
- dystrophic calcification
-CI
can cause angina ( heart pain due to lack of o2)
Bronchogenic carcinoma (primary)
- emphysema
- lung collapse
-active CI
- bronchiectasis
-haemosiderosis
-anthracosis
- -bening neoplasia
- coag necrosis
- haemorrhage
- malignant
- ulceration
secondary carcinoma of the lungs (lymphatic permeation)
- emphysema
- haemosiderosis
- anthracosis
- neoplasm- invasion
- abnormal mitotic activity
- invasion
-TAIR
- coag necrosis
- haemorrhage
- thickened pleura
-fibrosis
-granulation tissue
- consolidation
Secondary Melenoma of the brain
- neoplasia
-coliq necrosis
- coag. necrosis (of tumour)
-tumour associated immune response (type of CI- aggregates of lymphocytes)
-invasion
-haemorrhage
- extra and intra cellular melanin-browninsh
- increased NC ratio
IN MORBID
- multiple tumours
- multiple tumours
-does not resemble the surrounding tissue
Stomach
Chronic peptic ulcer
- ulceration
-congestion
- active CI
- coag necrosis
- haemorrhage
- Thrombosis
- large excavation
- very little mucosa seen
- collagen, vascular sprouts, fibroblasts
Acute Trachitis morbid
-AI
- congestion of BV
- loss of mucosal folds
- exudate fomration
-oedema
Morbind Infarct
- thickening of myocardium -hypertrophy
- thrombosis of arteries
-coag necrosis
- infarction
-AI
- granulation tissue
- fibrosis
Infarct
Left Ventricle Hypertrophy Morbid
- pathological hypertrophy
-mitrial valve insufficent- backflow
- thickness increases to 3-4cm
fungating primary cervical carcinoma- Morbid
- no capsule
-necrosis
pseudocapsule
-invasive
primary scirrhous carcinoma- morbid
- stony hard
-invading
-no capsule
- haemorrhage
Haemorrhagic infarct of brain Mobid
-haemorrhage
-coliq necrosis
- red infarct
-some restoration of blood flow
- apoptotic cysts
ruptured aneurysm and thrombosis of the descending aorta- morbid
- see anurysm
-haemorrhage
-atherpscelrosis
- thrombosis
- abnormal dilaition of blood vessel
Kidney- benigny hypertension- morbid
-atrophy
-scaring
-small hemorrhages- purpura
- small size
- looks granular
Abdominal Aorta- atheroscelrosis and complicated plaques- Morbid
- complicated atheromatous plaques
- dysrophic calcification
-ulceration
-cholesterol emboli
-thrombosis
-aneurysm
-haemorrhage
Artery- atherosclerosis and thrombus- morbid
-atheroscelrosis
-thrombus- mixed- lines
chronic peptic ulcer- morbid
- flat ulcer crater
- mucosa ajacent to ulcer is flat
- mild gastritis
-perfusion
- not cancer because no tumour mass
Primary carinoma of bronchus- morbid
- emphysema
- thombosis
-ahthrocosis
- single mass
- on bronchus
- coag necrosis
-bronchioecstasis
Lymphatic permeation of secondary carcinoma
-lymphatic permeation
-anthracosis
-spread through sub pleural lymphatics
- abnormal mitotic figures
- pleomorphic cells
- anthracosis
-emphysema
- haemorrhage
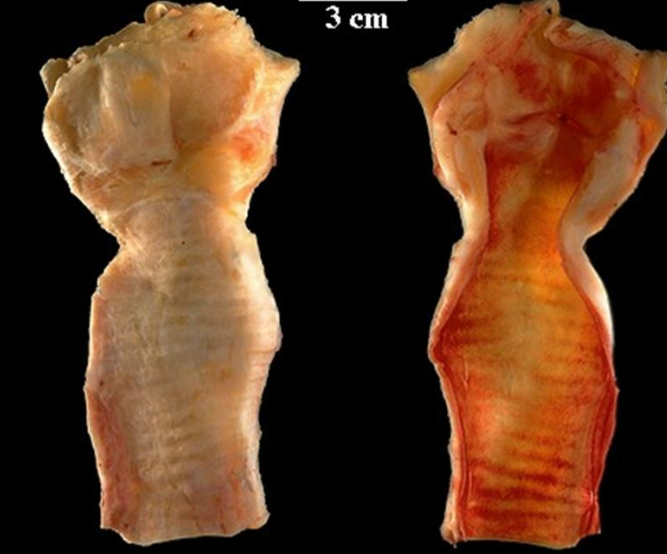
Coagulative necrosis of Kidney
Pale necrotic regions due to iscemia


New Note
New Note

Grey hepatisiation

New Note

New Note

Healing mycardial infarct
coag necrosis
haemorrhage
fibrosis
left ventrical hypertophy

New Note

Milliary tb in foetal lungs

New Note

fiberomyeloma-morbid

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note
New Note
New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note
New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

New Note

sclerosis
hardening/ thickening of body tissue
-causes deposition of mineral salts causing scaring
progressive with connective tissue diseases
lipodystrophy
loss of fat due to failed fat metabolism
can be localised
can be to do with other diseases i.e. diabetes
Reiter's Syndrome
reactive arthritis
immune response-i,e STI, salmonella and shigella
affected people have HLA-B27 on CH 6
pilonidal sinus
aka cyst
frequent in hairy young males
small skin sac in the base of the spine
only causes problem if becomes infected causing pus, swelling and pain
Angioma
non cnancerous benihn growth of small blood vessels,
can be spider veins ect
on brain or gastric can cause bad bleeds/anaemia.
gangrene
death of tissue
secondary to growth of bacteria
often in extremities
fever, pain, darkening of skin, unplesent odour
Metabolic
Diabetes Mellitus
decreased rate of insulin production
leading cause of western death
beta cell failure
T1- juvenile/insuline dependent
T2- no inuline dependent
acidosis (can give sodium bicarbonate) respiratory or metabolic
Alkalosis (metabolic or . respiratory)iv acid componsnets
oedema
accumulation of fluid in the tissue
can be generalised or localised.
ie. pulmonary oedema- blood/fluids accumulating in the lungs.
immune/ lymphatics
Hodgkins Lymphoma
common
young/mid life
in lymph-nodes/ enlarged
does not spread- only one group of nodes to another
Non Hodgkin Lymphoma
malignant
aberage 50y old
more common
Sarcoidosis
systemic inflammation from unknown origen
often detected in xray
enlargement of lymphnodes
red skin rash
can affect other organs treatment with antiinflams (steroids) or in some cases with immunosup.
Scleroderma
increasing amounts of fibrous depositions within tissue, skin and other organs.
can lead to raynauds phenomenon
Rheumatoid Arthritis
AI disease causing inflammation through synovial joints (fingers wrists, toes, ankles, elbows) causing pain and smelling
Kawasaki's disease
children under 5
inflammation of skin and mucosal membranes
enlarged lymph nodes
treatment with anti inflams
Lupus
Erythematous- CT disease
Systemic Erythematous- not only skin, all organs
thickened reddish patches on skin, fatigue, fever, weight loss, arthritis
Encephalitis
inflamation of brain
can cause swelling (cerebral oedema)
can be caused by various viruses.
Bells Palsy
paralysis caused by swelling or cutting of facial nerves
dropping and distorted features, can be recovered.
Dysphagia
inability to sleep due to damage to the brain
hypothyrodisim/ myxedema
reduced level of thyroid hormones
patients experience puffy thickening of skin, lips, fingers, lehs
lethergy, weight gain, hair loss
Graves disease/ hyperthyroidism
toxic diffuse goiter
ai disease
swelling, rapid heartbeat, sweating, weight loss, fatigue
can also develop exopthalomas- protruding eyeballs.
Hashimotos disease
slow developing persistent inflammation of the thyroid gland
can press on trachea and cause pain/ difficulty breathing.high levels of thyroid antibodies.
spina bifida
abnormal formation of neural tubes in embryonic development
weakness in feet
lack of reflexes
fatty depostis on skin
mastitis
inflamation caused by infection often due to cracked nipple from brestfeeding
can also be due to hormonal imbalance
tachycardica
paroxysmal
heart rate elevated- 140-220bpmventricular tachycardia is more serious ad can cause chest pain and breathlessness
asthma
contraction of the bronciole
increased mucous production
1/20 people
treatment with bronchiodilators- salbutamol
ascites
accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity
cirrhosis
death of liver cells followed by fibrious tissue formation.
can be due to excessive alcoholism, poor diet.
hepatitis
causes hepatic inflammation
reduced functionality
jaundices, abdo pain, nausea
can be transmitted depending on type