Light
The Light
Electromagnetic radiant energy (whole spectrum)
Visible Light
Different wavelengths represent different colors
Light Stimulus
Any light stimulus characterized by the following:
* They are all independent or orthogonal to each other*
* They are all independent or orthogonal to each other*
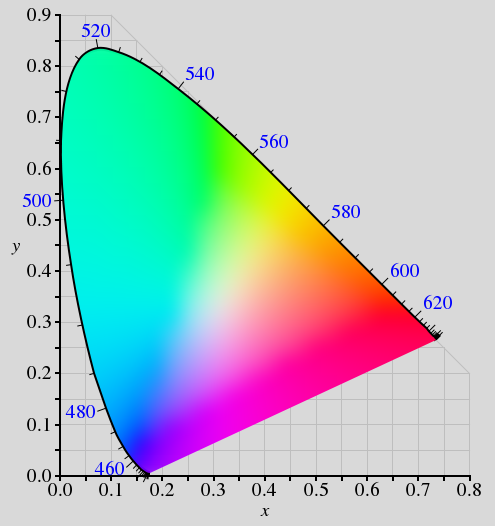
CIE Wave Diagram

Hue
- The dominant wavelength
- Used like "color" in everyday conversation
Saturation
- Wavelength Percentage
- Mix colors to make other colors
Brightness
- Light intensity
- The amount of luminance that the color has, determined by amplitude
Primary Colors
- Depends on the colors you mix.
Subtractive Process
- Mixing colors/paint
- Putting one color on another you remove the affect of the first color
- Red/Yellow/Blue
Additive Process
- Adding lights
- Use Red/Green/Blue
Features of CIE
- Border - same as visual spectrum
- All points on the curve are called pure/spectral colors, all points on the straight line are called pure non-spectral colors (purples)
- Saturated colors are in the middle of the enclosure
- The amount of gray or white achromatic light is the third dimension ont he diagram